Show HN: Survey on AI Agents in Production (324 Respondents)
AI Agents and the Future of Business
Chapter 1: What Are AI Agents?
AI agents are not just chatbots or automation scripts. They are advanced systems that can interpret complex inputs, make decisions, and sometimes even execute tasks independently. They are designed to reason, learn, and adapt based on goals and real-time feedback.
Key Characteristics:
- Autonomy: AI agents can function with minimal human intervention.
- Goal-Oriented Reasoning: They operate under clear objectives.
- Contextual Awareness: They can filter out noise and focus on relevant signals.
- Safety & Interpretability: They are designed to minimize harmful or biased outputs and provide transparency in decision-making.
Why This Matters:
AI agents offer more than just automated chat or rote scripting. By operating with an internal model of the world, they can handle tasks once demanding human judgment and domain knowledge. This shift is already evident in areas like code generation, customer support, and advanced analytics.
Chapter 2: Who's Driving AI Agents?
AI agents are being adopted by a wide range of roles, company sizes, and industries.
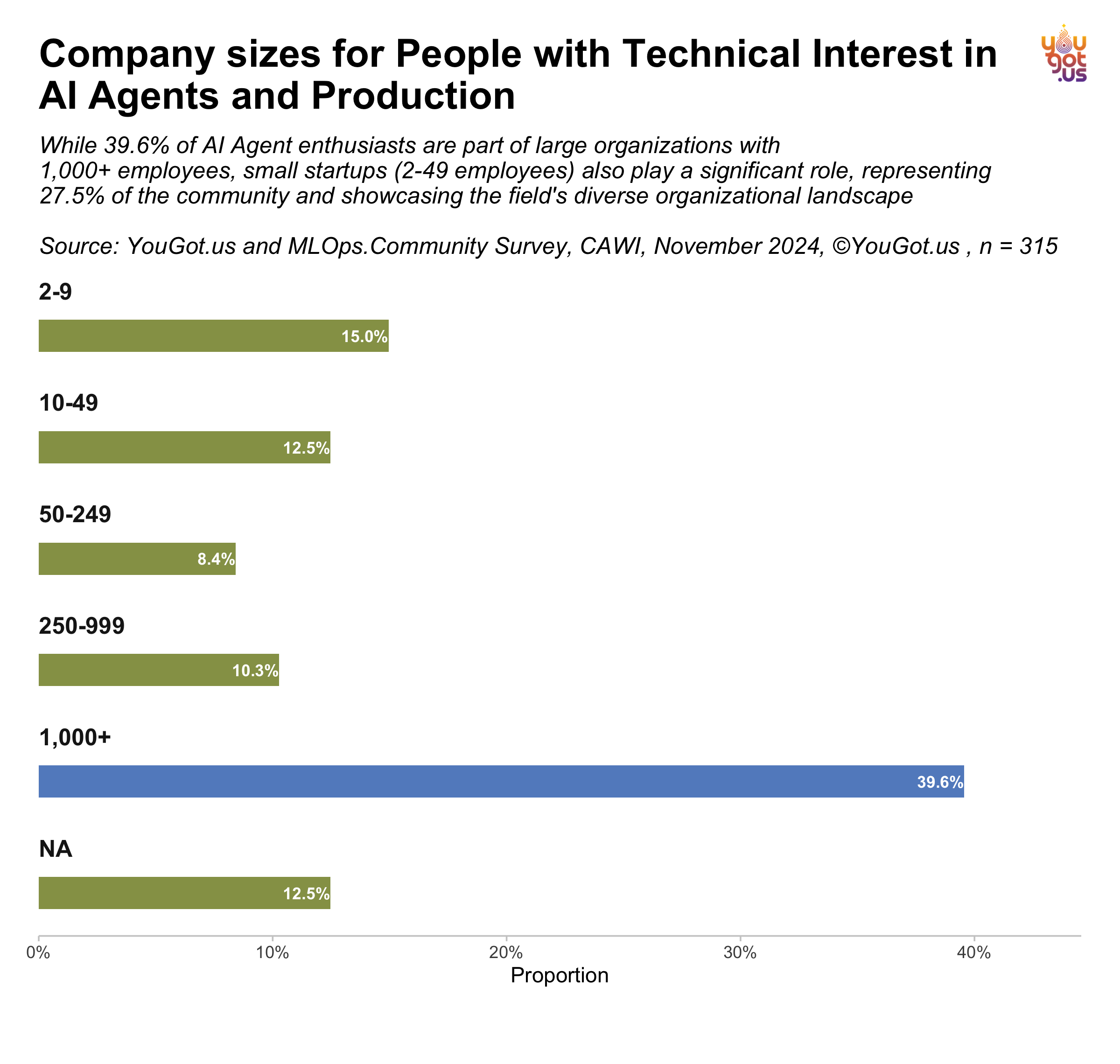
Company Sizes:
The YouGot.us survey shows that both startups and large enterprises are investigating AI agent solutions. Bigger companies benefit from robust infrastructure and capital, while startups have greater agility in experimentation.
The Roles Behind AI Agents:
- AI/ML Engineers: Deep technical expertise
- Software Engineers: Bridge the gap between research and production
- Founders, CTOs: Guiding strategy and direct implementation
- Business/Marketing/Sales: Resonating across diverse functions
- Data Scientists: Broader scope of analytics and AI experimentation
Roles Vary by Company Size:
Early-stage organizations rely on multi-skilled personnel, while larger enterprises invest in specialized talent to handle complex data, compliance, and organizational structures.
Leading AI Agent Industries:
Technology leads the pack, followed by finance, retail & e-commerce, and healthcare. Each industry has unique drivers and challenges for AI agent adoption.
Chapter 3: The Current State of AI Agent Adoption
AI agent adoption is still nascent, with many organizations in early stages of experimentation. However, a growing number are reporting moderate or extensive adoption.
Early-Stage Startups vs. Enterprise:
50% of startups report full AI agent integration, while only 6% of Fortune 1000 companies have achieved this level of adoption. Startups are more agile and willing to take risks.
Why Organizations Are Adopting AI Agents:
Improving operational efficiency and automating repetitive tasks are the primary motivations. Other reasons include enhancing customer experience, reducing operational costs, and innovating products and services.
From Pilots to Production:
Scaling up from pilot to full deployment involves technical, strategic, and cultural challenges. These include integrating with existing systems, securing leadership buy-in, and addressing security concerns.
Shifting Priorities: Cost Reduction and Efficiency on Top:
In the next year, organizations expect AI agents to become increasingly essential. Cost reduction and operational efficiency are now top priorities as companies seek to stay lean in uncertain economic times.
Chapter 4: Key Use Cases and 2025 Focus Areas for AI Agent Projects
Current Usage:
The most commonly adopted use cases are internal knowledge management, customer support, and coding assistance.
Looking Ahead: Usage Goals Over the Next Year:
Organizations plan to expand the use of AI agents into new domains, such as process optimization & automation, HR & employee support, and marketing automation & lead generation.
Divergent Approaches: Startups vs. Fortune 1000:
Startups prioritize marketing automation and project management for agility and customer-facing innovation. Fortune 1000 companies focus on personal productivity and content creation for incremental improvements and scalable operations.
Use Case Summaries and Key Takeaways:
Coding assistance and internal knowledge management have shown significant ROI. The hybrid approach of AI agents and human agents is proving effective in customer support. The divide between startups and large enterprises reflects differing risk tolerance and priorities.
This survey highlights the growing adoption and potential of AI agents across industries. From improving efficiency to innovating products, AI agents are poised to transform the way businesses operate in the years to come.